

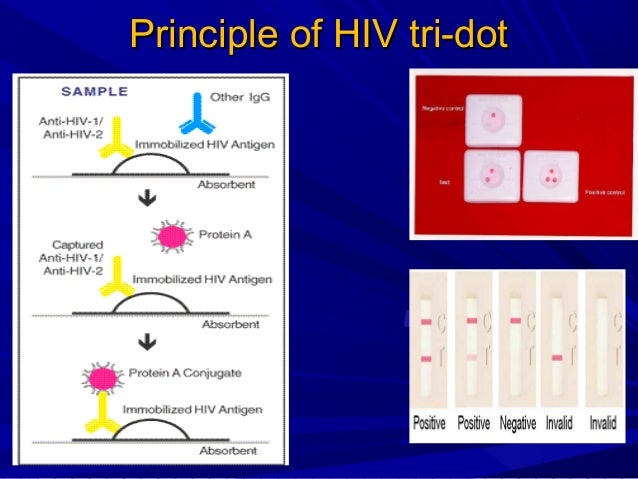
Both assays were more sensitive, in the detection of the specific antibody response, when used among the paediatric cases of NCC who had multiple brain lesions (100%) than when used among the single-lesion cases (87%). The corresponding values for the dot-blot assay were similar, at 89%, 73%, 72.5%, 89%, 82%, respectively. When used with these thresholds, the ELISA gave a sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values and diagnostic efficacy of 89%, 81%, 79%, 90%, 85%, respectively. Analysis of antibody response indicated that the optimum threshold titres for seropositivity were 1:800 for the ELISA and 1:6400 for the dot-blot assays. Most (86%) of the cases of NCC had presented with focal seizures. Here we show that the widely used Bicinchoninic Acid (BCA) assay tends to underestimate protein concentrations of tissue samples. Another 100 sera, from children who had tubercular meningitis (N=20) or a parasitic disease other than taeniasis/cysticercosis (N=20) or, apart from a minor respiratory-tract infection, appeared healthy (N=60), were also investigated. Despite the availability of a wide range of commercial kits, protein quantification is often unreliable, especially for tissue-derived samples, leading to uneven loading in subsequent experiments. Eighty of the subjects (20 aged 5-<8 years and 60 older children) each had the signs and symptoms of NCC, including one brain lesion (N=69) or multiple brain lesions (N=11) that were visible by computed tomography. In this regard, it should be noted that, to generate the negative controls, a condition is used under which AAV viral genomes exponentially replicate in the absence of the capsid VP3 protein. In the present study, the performances of an ELISA and dot-blot assay, for the detection of antibodies against antigens from larval Taenia solium, were investigated and compared, using sera, from children aged 5-12 years, that were diluted to at least 1:400. Therefore, the dot blot assay by itself cannot exclude the possibility that capsid assembles to a level below the sensitivity of the assay. Immunoblotting is now widely used in conjunction with two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, not only for traditional goals, such as the immunoaffinity identification of proteins and analysis of immune responses but also as a genome-proteome interface technique.Although human neurocysticercosis (NCC) is being increasingly recognized in children, diagnosis of the disease can be difficult, and the 'gold standard' criteria that indicate an unambiguous case have still to be established. Dot blot is a simplified procedure in which protein samples are not separated by electrophoresis but are spotted directly onto membrane. When the ligand is not an antibody, the reaction can be visualized using a ligand that is directly labeled. The membrane is overlaid with a primary antibody for a specific target and then with a secondary antibody labeled, for example, with enzymes or with radioisotopes. Proteins are typically separated by electrophoresis and transferred onto membranes (usually nitrocellulose). It involves the application of a small amount of sample directly onto a membrane, which is then probed with a specific antibody or nucleic acid probe to detect the target molecule. They involve identification of protein target via antigen-antibody (or protein-ligand) specific reactions. A Dot Blot technique is a simple and quick immunoassay that may be employed to determine if your antibodies and detection system are effective. Immunoblotting techniques use antibodies (or other specific ligands in related techniques) to identify target proteins among a number of unrelated protein species.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
